Google indexing works by crawling web pages, processing their content, and adding them to its database. This process helps users find relevant information quickly.
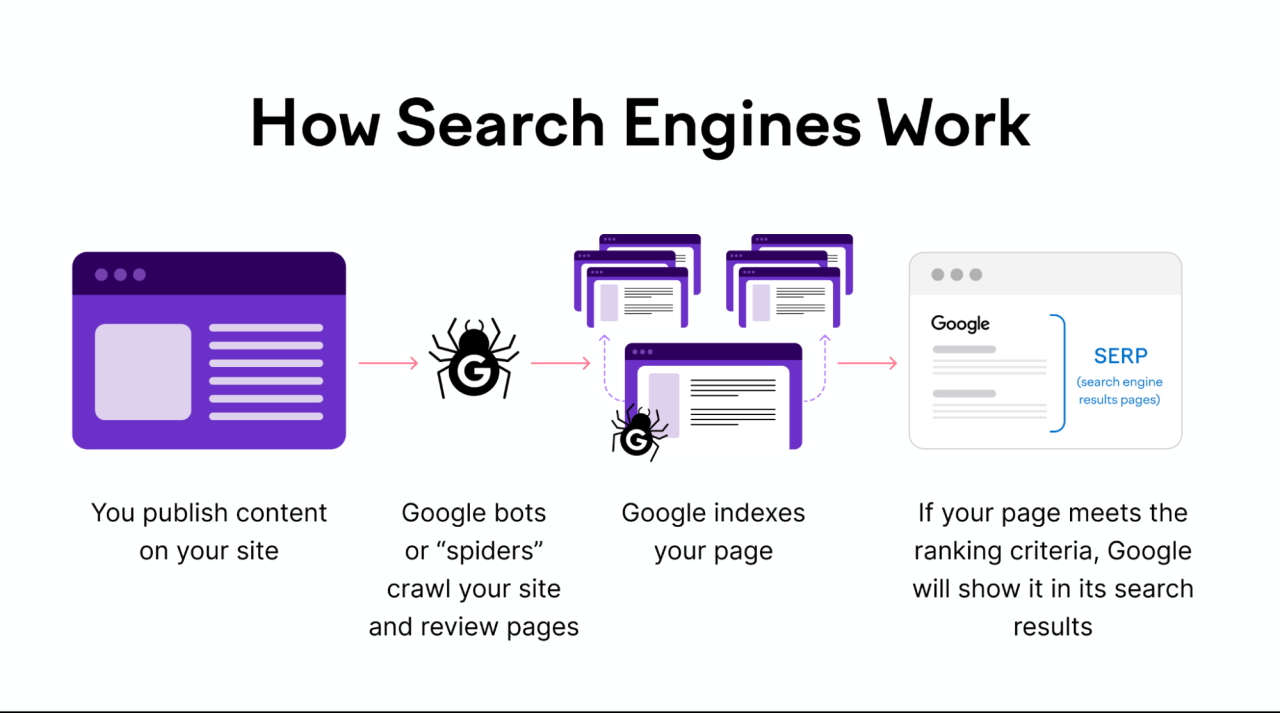
Understanding how Google indexing works is crucial for website owners aiming to improve their online visibility. Google’s process begins with crawling, where bots, known as spiders, scan web pages for new or updated content. These bots follow links and gather data from each page they visit.
Next, Google processes the collected information, analyzing the content, keywords, and structure. This step ensures that the content is relevant and valuable. Finally, the data gets added to Google’s index, making it searchable for users. Proper indexing leads to better search rankings, driving more organic traffic to your site.
Mini Package

- You can add 3 Websites
- Index 200 Pages Per Day
- Total 6000 Pages or Posts
- Bulk Indexing
- Monthly Reporting
- Add 2 Google Accounts
What Is Google Indexing?
Google Indexing is a crucial part of how search engines work. It involves storing and organizing web pages to make them searchable. Without indexing, users wouldn’t find relevant results in search queries.
Definition And Importance
Google Indexing refers to the process of adding web pages into Google’s search database. When you create a new website or update an existing one, Google needs to index it to make it searchable.
Indexed pages appear in search results, while non-indexed pages do not. The importance of indexing lies in its ability to make your content discoverable. If your site isn’t indexed, it won’t show up in search results. This means less traffic and fewer visitors.
Here’s why Google Indexing is essential:
- Visibility: Indexed pages are visible in search results.
- Traffic: More indexed pages mean more potential visitors.
- Revenue: Higher traffic can lead to increased sales and revenue.
How It Differs From Crawling
Crawling and indexing are two different processes. Crawling is the first step, where Google bots scan the web to find new or updated pages. These bots, also known as spiders, follow links from one page to another.
Once a page is crawled, Google decides whether to index it. Indexing involves analyzing the page’s content, keywords, and metadata. If deemed valuable, the page gets added to Google’s index. This is where it becomes searchable.
To summarize:
| Process | Action |
|---|---|
| Crawling | Scanning web pages for new or updated content. |
| Indexing | Storing and organizing the scanned pages in Google’s database. |
Understanding the difference helps in optimizing your site better. Ensure your site is easy to crawl and index for improved search visibility.

Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
The Crawling Process
The crawling process is the first step in how Google indexes web pages. It involves Google discovering new or updated pages on the web. This is crucial for ensuring that your website appears in search results. Below, we delve into the details of this process.
Googlebot Explained
Googlebot is Google’s web crawler. It scans the web for new and updated content. This bot is an automated software used by Google. It finds and reads web pages. Googlebot visits websites and follows links on those pages. The information it gathers is then used to update Google’s index.
Googlebot has two main types: desktop and mobile. The desktop Googlebot mimics a user on a desktop computer. The mobile Googlebot mimics a user on a smartphone. This helps Google understand how different users experience the web.
| Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Desktop Googlebot | Mimics desktop users |
| Mobile Googlebot | Mimics mobile users |
Crawl Budget Management
Crawl budget refers to the number of pages Googlebot crawls on your site. This budget is important for large websites. Google prioritizes crawling based on a website’s importance and freshness. The more important or frequently updated your site, the higher its crawl budget.
Several factors impact your crawl budget:
- Site popularity
- Server performance
- Internal linking structure
To manage your crawl budget, optimize your website’s structure. Ensure fast server response times. Remove unnecessary redirects and broken links. This helps Googlebot crawl your site efficiently.
By understanding the crawling process, you can improve your website’s visibility. This starts with knowing how Googlebot works and managing your crawl budget effectively.
How Google Indexes Pages
Understanding how Google indexes pages helps improve your website’s visibility. The indexing process involves several steps. These steps ensure that your content appears in search results. Let’s dive into the details of Google indexing.
Content Analysis
Google starts by analyzing your page content. The Googlebot crawls your website. It reads the text, images, and other media. It checks your HTML tags like and descriptions. These tags help Google understand what your page is about.
Google also looks at your keywords and their placement. Keywords should be in your headings, subheadings, and body text. This helps Google know the main topics of your page. Use relevant keywords but avoid keyword stuffing.
Google also assesses the quality of your content. Content should be original, informative, and useful. High-quality content ranks better in search results.
Handling Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can confuse Google. It may not know which version to index. This can hurt your website’s ranking.
To manage duplicate content, use tags. These tags tell Google which page is the original. You can also use 301 redirects to point to the original page.
Google also uses algorithms to detect duplicate content. It tries to show the best version in search results. Ensure your content is unique to avoid ranking issues.
Here are some tips to avoid duplicate content:
- Write original content.
- Use tags.
- Use 301 redirects for moved pages.
- Avoid copying content from other sites.
Google indexing is complex, but understanding these steps can help. Focus on content analysis and managing duplicate content for better rankings.
Optimizing For Indexing
Optimizing your website for indexing is crucial for Google to understand your content. Proper optimization helps search engines crawl and index your site efficiently. This section will guide you through essential steps for ensuring your site is indexed correctly by Google.
Xml Sitemaps
An XML Sitemap is a file that lists all pages on your website. It helps search engines find and index your content faster. Creating an XML Sitemap is simple and can be done using various tools.
- Use tools like Yoast SEO or Google XML Sitemaps to generate the sitemap.
- Ensure your sitemap includes URLs for all key pages and posts.
- Submit your XML Sitemap to Google Search Console.
Submitting your sitemap ensures Google knows all the pages on your site. This improves your chances of being indexed efficiently.
Robots.txt Configuration
The robots.txt file tells search engines which pages to crawl and which to ignore. Proper configuration is vital for effective indexing.
Here’s how to configure your robots.txt file:
- Create a text file named robots.txt in your root directory.
- Add rules to allow or disallow specific pages or directories.
- Use the following syntax for rules:
User-agent:
Disallow: /private/
Allow: /public/page.html
The User-agent specifies the crawler. The Disallow and Allow directives control access.
Ensure essential pages are allowed and sensitive pages are disallowed. Incorrect configuration can block important content from being indexed.
Check your robots.txt file using Google Search Console’s robots.txt tester. This helps you identify and fix any issues quickly.
Monitoring And Troubleshooting
Monitoring and troubleshooting Google indexing is crucial for website health. Proper monitoring ensures that your pages are indexed correctly. Troubleshooting helps identify and resolve indexing issues. This section will guide you through using Google Search Console and identifying common indexing issues.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free tool from Google. It helps you monitor your website’s presence in Google search results. Here’s how to use it for indexing:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
- Select your website property.
- Navigate to the “Coverage” report.
- Check for any errors or warnings.
The “Coverage” report shows which pages are indexed. It also shHow Google Indexing Workszzows why some pages are not indexed. You can see details like:
- Valid pages
- Excluded pages
- Pages with errors
To fix issues, click on the error message. Google will provide details and suggestions.
Common Indexing Issues
Here are some common indexing issues you might encounter:
| Issue | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Blocked by robots.txt | The page is blocked from indexing. | Update your robots.txt file. |
| 404 Error | The page does not exist. | Create or redirect the missing page. |
| Duplicate Content | Multiple pages with the same content. | Use canonical tags to specify the main page. |
Regular monitoring and prompt troubleshooting can keep your site healthy. Always use Google Search Console to stay updated.

Credit: www.thebricks.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Google Indexing?
Google Indexing is the process by which Google bots crawl, analyze, and store web pages. This makes them searchable on the search engine.
How Does Google Crawl Websites?
Google uses automated bots called spiders or crawlers to scan websites. These bots follow links and gather data for indexing.
Why Is Indexing Important For Seo?
Indexing ensures that your web pages are searchable on Google. Without indexing, your site won’t appear in search results.
How Often Does Google Index Websites?
Google continuously indexes websites, but the frequency can vary. It depends on factors like site updates and crawl budget.
Conclusion
Understanding Google indexing is crucial for your website’s success. Follow these steps to improve your site’s visibility. Regular updates and quality content are key. Stay informed about indexing changes to maintain your SEO efforts. Implement these strategies for better search engine rankings and increased traffic.
Happy optimizing!